Earth/matriX
Science Today
|
 |
 |
|||
Our Price |
Our Price $8.99 Purchase in Amazon |
Our Price Paperback In Stock |
||
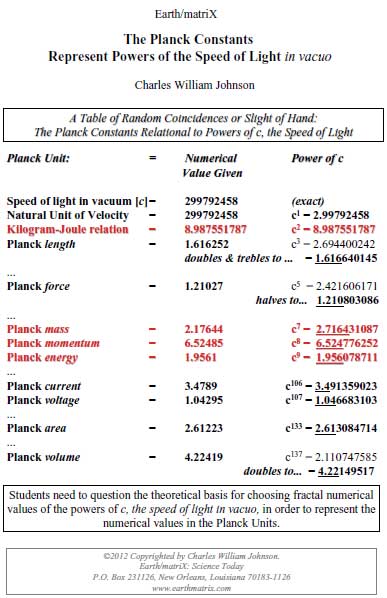
The physics paradigm today is based mainly upon the concept of c-square, the squaring of the speed of light in a vacuum. Numerous fundamental physical and chemical constants provided in the physics literature [CODATA] reflect numerical values based upon powers of c, the speed of light in vacuo. The speed of light in a vacuum is determined to represent the upper limit of movement of mass|energy by physicists. |
The upper speed limit for a light photon is 299792458 meters/second. The square of that number produces a numerical value that does not exist in any form of matter-energy. The c-square actually represents a number that corresponds to a near massless event: a light photon. The author goes beyond a critique of Albert Einstein’s famous formula based upon this unreal number. The rejection of Einstein’s formula is explored through basic math, the summation of powers in the equation’s terms. |
A common procedure followed in deriving many of the CODATA recommendations is to divide certain fundamental physical constants by the value of the elementary charge, e, 1.602176487. With regard to the Planck constants and units of measurement, the case is argued that Max Planck may have simply reversed engineered this procedure in order to derive his natural units. |
Earth/matiX
SCIENCE TODAY
©2012 Copyrighted by Charles William Johnson. All rights reserved.
Earth/matriX: Science in Ancient Artwork. ISBN 1-58616-451-1
Earth/matriX Editions P.O. Box 231126 New Orleans, LA 70183-1126
email:johnson@earthmatrix.com
| Home | Books | All Essays | Author |